Open DNS
Determine if TCP or UDP port 53 for DNS is open to the public
While some ports such as HTTP and HTTPS are required to be open to the public to function properly, more sensitive services such as DNS should be restricted to known IP addresses.
Recommended Actions
Follow the appropriate remediation steps below to resolve the issue.
Log in to the AWS Management Console.
Select the “Services” option and search for EC2.
Scroll down the left navigation panel and choose “Security Group” under “Network & Security”.

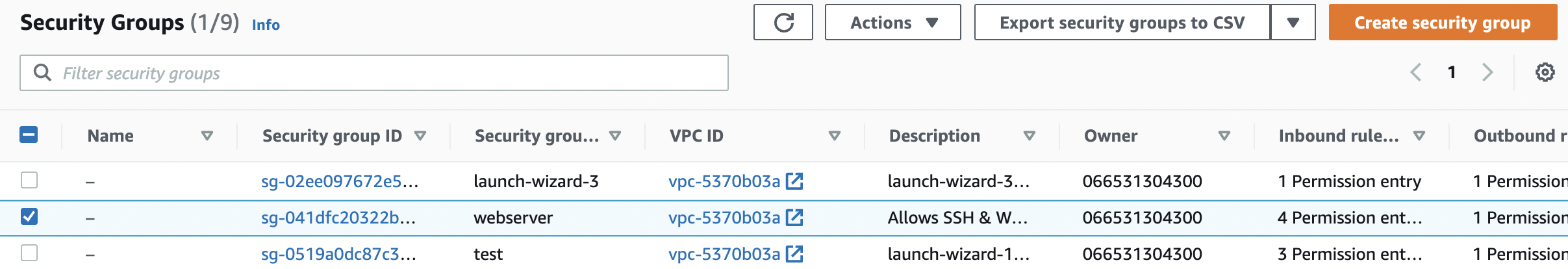
Select the “EC2 Security Group” that needs to be verified.
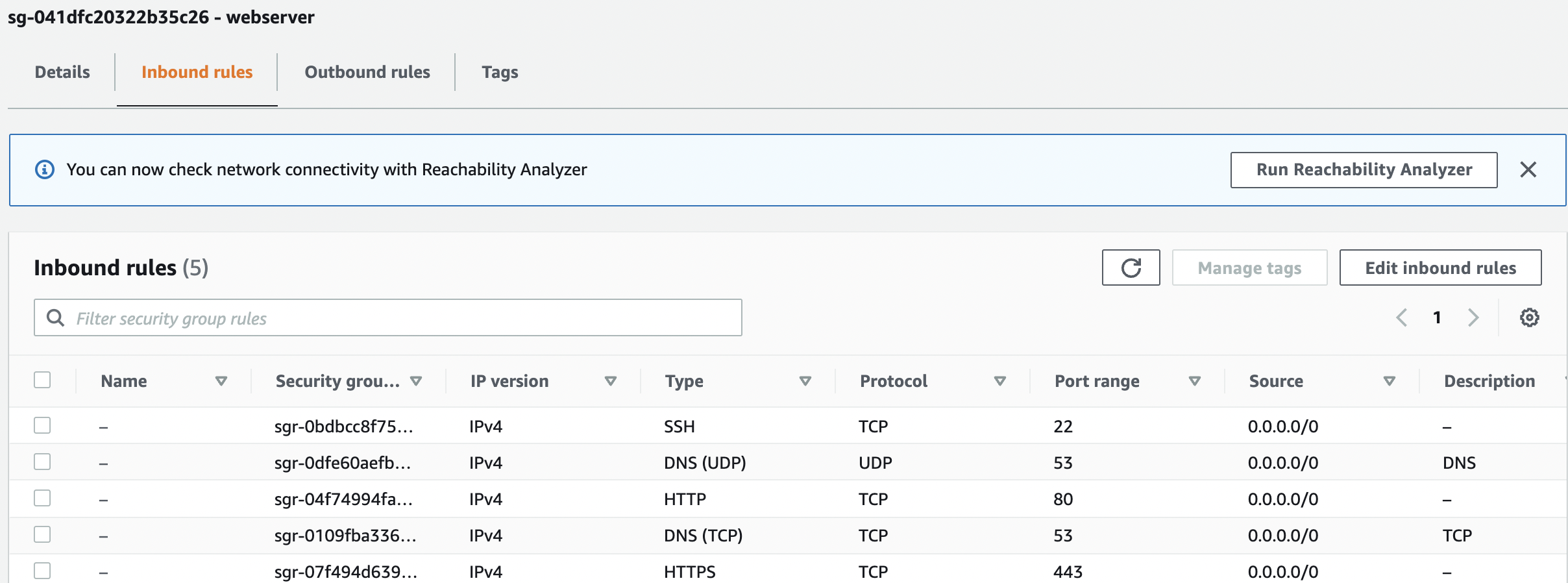
Scroll down the bottom panel and choose “Inbound rules”. Verify the value for “Source” column for “DNS(UDP)” or “DNS(TCP)” under “Type” and if any rule have value set to “0.0.0.0/0” or “::/0 " then the selected “Security Group” has “TCP/UDP” port 53 for “DNS” open to the public.
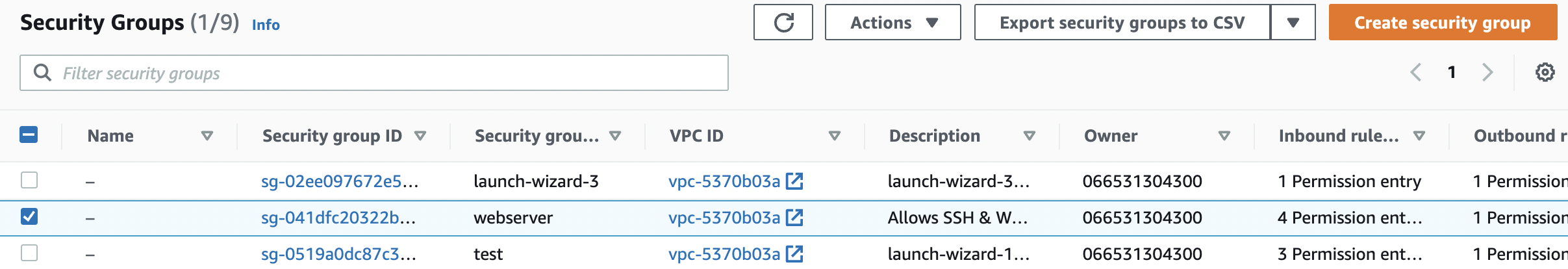
Repeat steps number 2 - 5 to verify other “Security Groups” in the selected AWS region.
Navigate to “Security Groups” under “Network & Security” and select the “Security Group” that needs to be modified to restrict the access of “TCP/UDP” port 53 for “DNS” to specific IP address.
Scroll down the page and select the “Inbound rules” and click on the “Edit inbound rules” button.
In the “Edit inbound rules” tab select either the “MyIP” or “Custom” from the “Source” column.
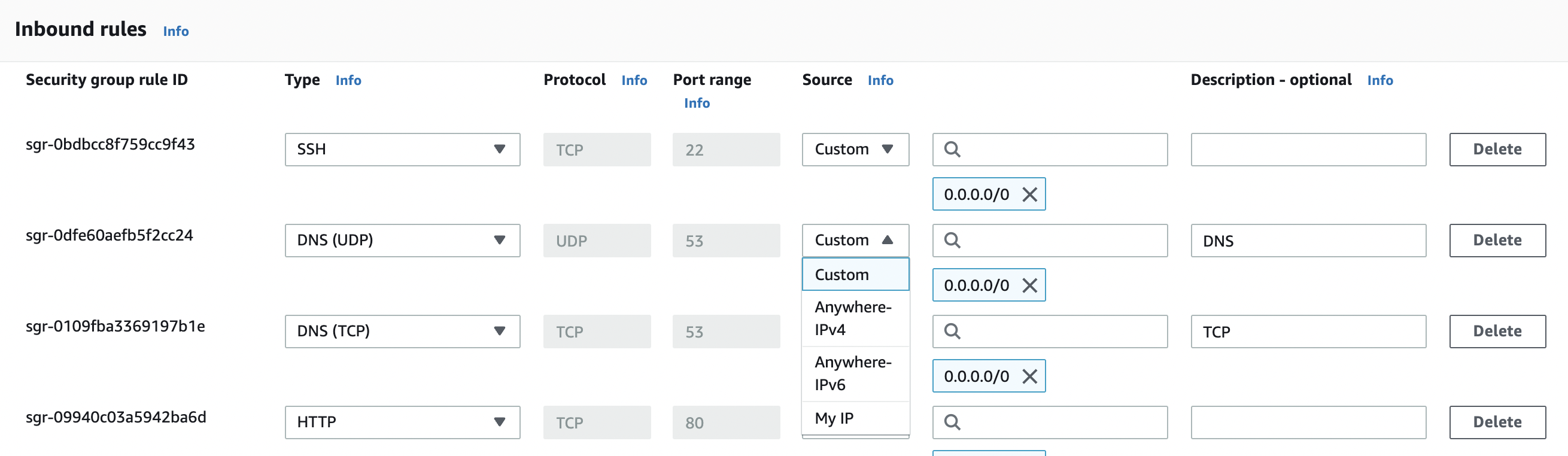
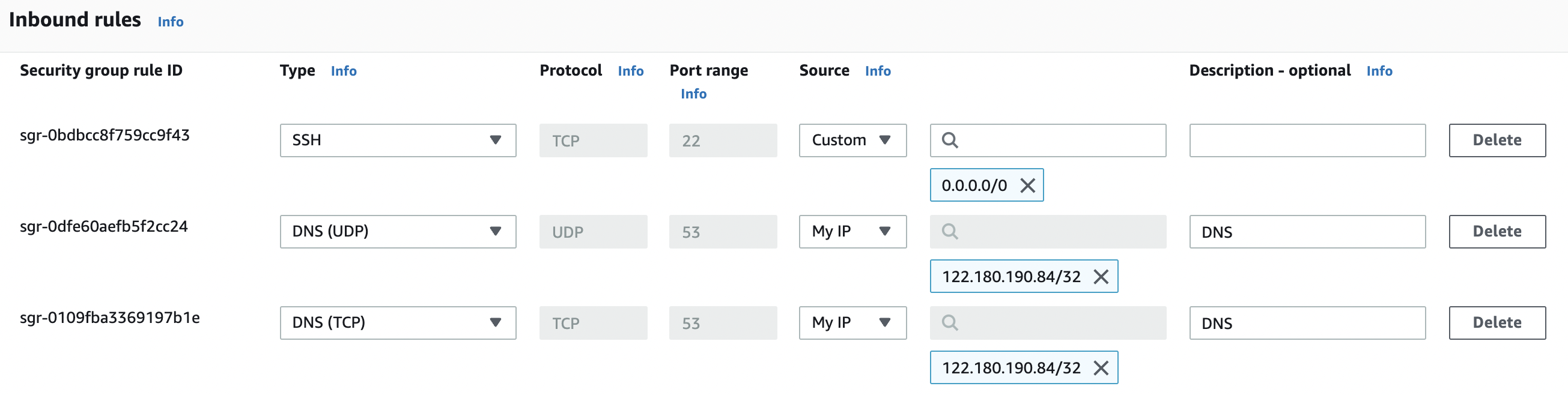
In the “Edit inbound rules” tab select the “MyIP” from the “Source” column to allow “TCP/UDP” port 53 inbound traffic only from your IP address.
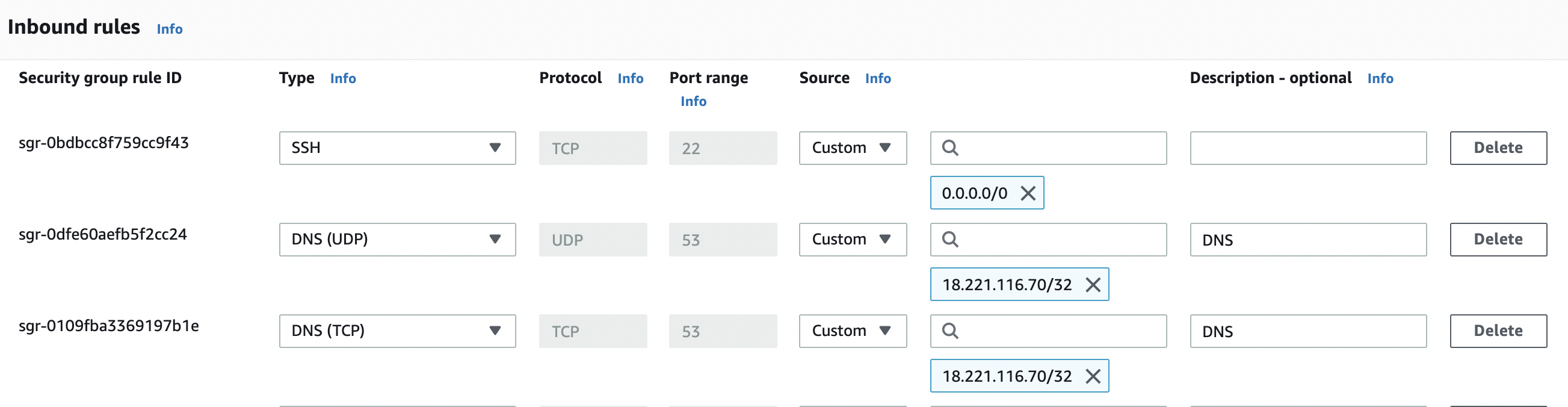
In the “Edit inbound rules” tab select the “Custom” from the “Source” column as per the requirements for “TCP/UDP” port 53 for “DNS” and specify static IP/Elastic IP address along with “Description” for the “Security Group” rule.
Click on the “Save rules” button to make the necessary changes.

Repeat steps number 7 - 12 to restrict “TCP/UDP” port 53 for “DNS” to known IP address.