Server Auditing Enabled
Ensures that SQL Server Auditing is enabled for SQL servers
Enabling SQL Server Auditing ensures that all activities are being logged properly, including potentially-malicious activity.
Recommended Actions
Follow the appropriate remediation steps below to resolve the issue.
Log in to the Microsoft Azure Management Console.
Select the “Search resources, services, and docs” option at the top and search for “SQL servers”.
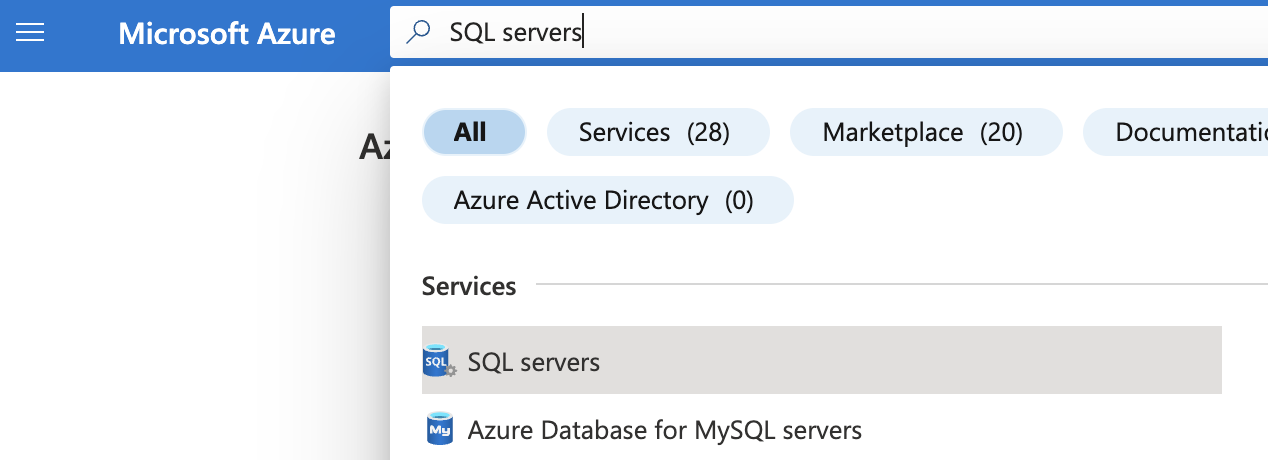
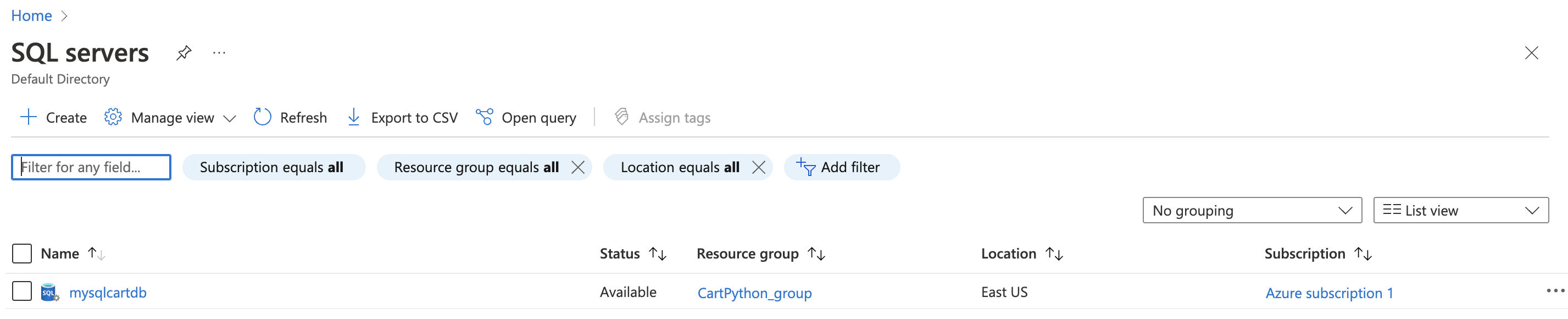
On the “SQL server” page, select the SQL server that needs to be examined.
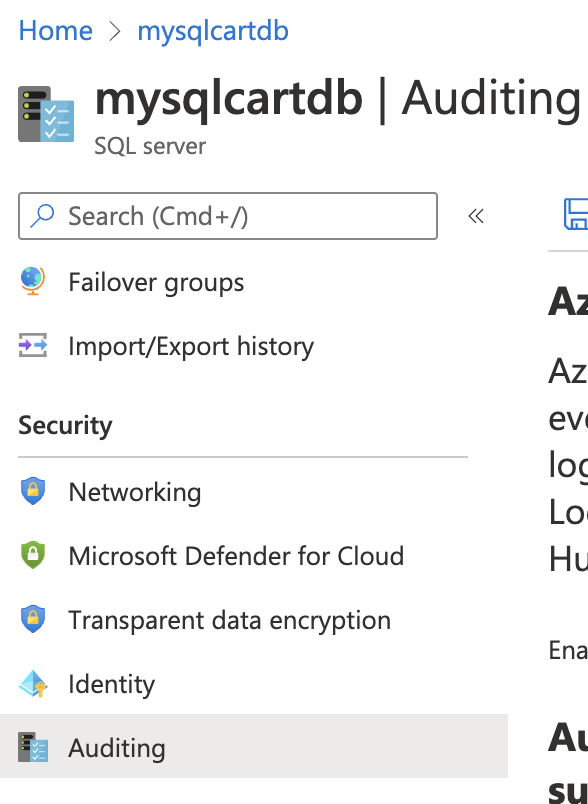
On the selected “SQL server” page, scroll down the left navigation panel and select “Auditing” under “Security”.
On the “Auditing” page, if “Azure SQL Auditing” and “Auditing of Microsoft support operations” is disabled then SQL Server Auditing for all activities are not being logged properly.
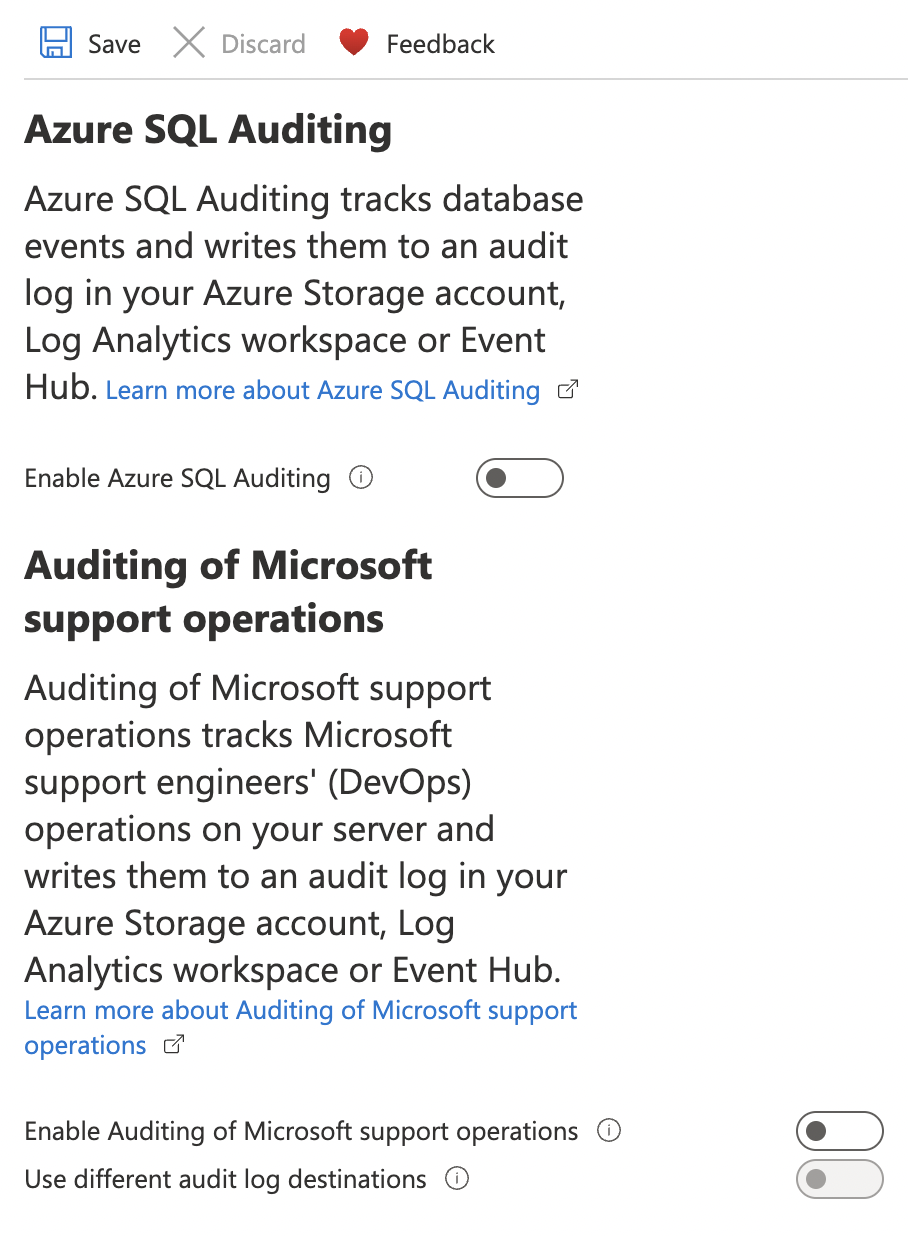
To ensure that auditing is enabled for each SQL server, go to “Auditing” page and turn the toggle “ON” for “Enable Azure SQL Auditing” and under “Audit log destination” checkmark “Storage”, “Log Analytics”, “Event hub” selecting the “Subscription” and “Storage end points” under each section.
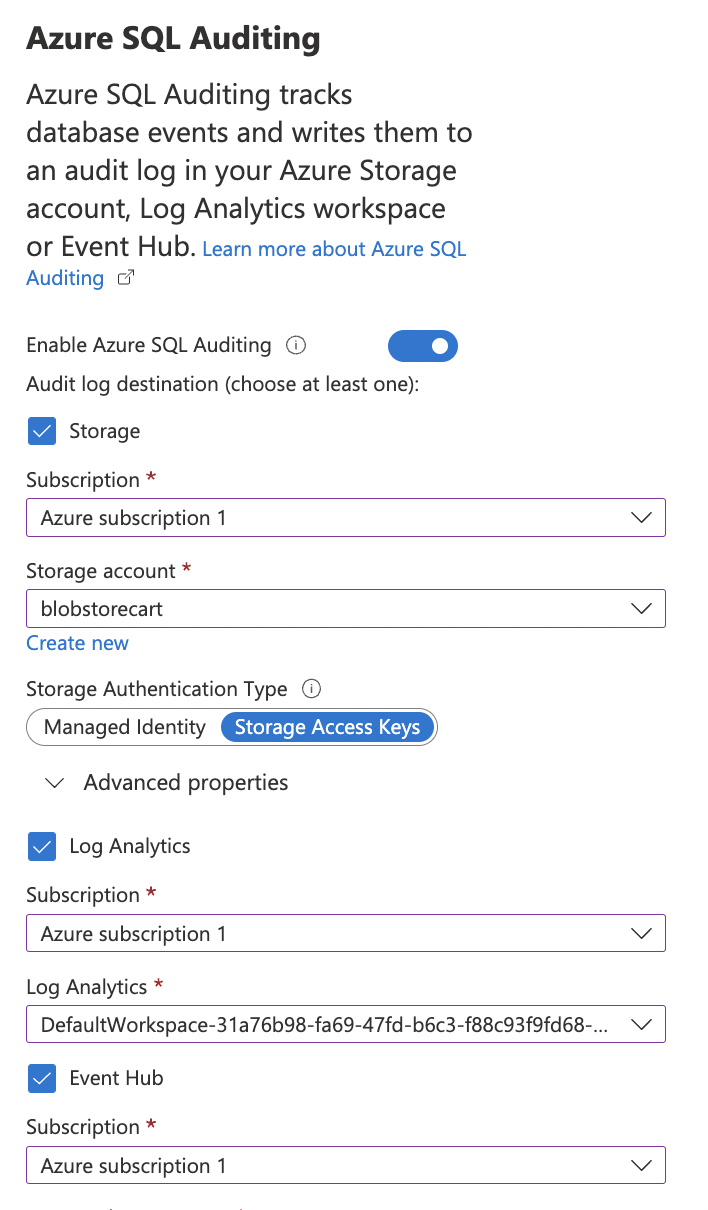
Turn the toggle “ON” for “Auditing of Microsoft support operations” and under “Audit log destination” checkmark “Storage”, “Log Analytics”, “Event hub” selecting the “Subscription” and “Storage end points” under each section.
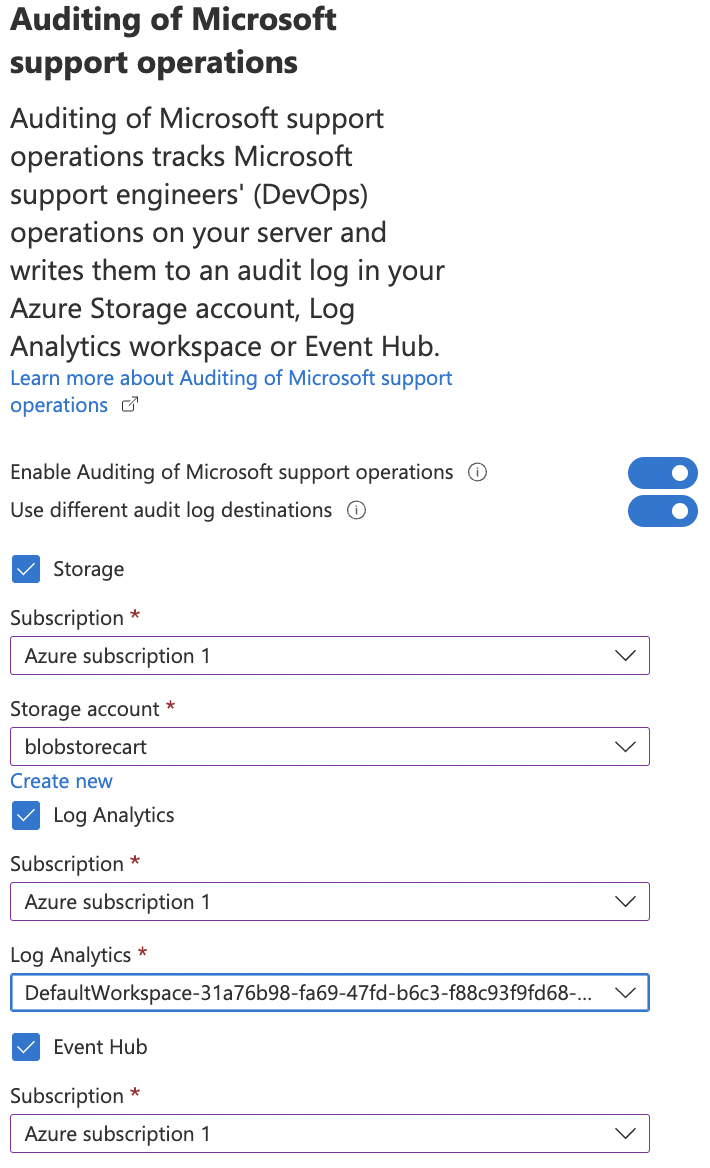
Click on “Save” at the top to make the necessary changes.
Repeat steps 3-8 to ensure that auditing is enabled for each SQL server.